
In the world of metal manufacturing, precision and versatility are non-negotiable. Cold Chamber Die Casting stands as a testament to achieving both. But what exactly is Cold Chamber Die Casting?
It is a process that handles alloys with high melting points and corrosive properties. A method embraced for aluminum and zinc alloys, brass, and copper. Visualize a technique that seamlessly blends metal powder with resin, conjuring castings that possess the allure of solid metal. This is the realm of Cold Chamber Die Casting.
In this blog, we embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of Cold Chamber Die Casting, exploring its myriad advantages, its meticulous process, and its diverse applications across industries.
Cold Chamber Die Casting Process and Tools

In the Cold Chamber Die Casting process, metal is liquefied in a highly high-temperature furnace and then dipped into a Cold Chamber infiltrated into the die. Let’s understand how it is done step by step-
Process:
1) Tooling and Mold Preparation:
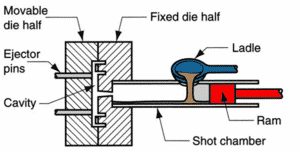
The first step of Die Casting starts with the design and fabrication of the mold, also known as die or tooling. The mold consists of the cover and the ejector. These two are precisely put in the Cold Chamber Die-Casting Machine to create the desired part shape.
2) Melting and Preparation of Metal Alloy
The metal alloy melts in a separate furnace, generally external to the Cold Chamber Die-Casting Machine. Once the metal reaches the desired temperature, it transfers to the Cold chamber of the die-casting machine.
3) Injection Phase
The molds are connected, creating a closed chamber. A hydraulic piston pulls molten metal from the Cold Chamber into the mold cavity. The metal fills the mold and solidifies rapidly due to the Cold Chamber’s lower temperature, which results in taking the shape of the part.
4) Cooling and Solidification
As the molten metal enters the mold, it cools and solidifies within seconds, and then the channels in it help to control the cooling process and prevent defects.
5) Ejection of the Part
Once it solidifies, the ejector part moves away from the cover die, and the portion that remains attached to the ejector is pushed out of the mold cavity.
6) Trimming and Finishing
If the part has any material attached, known as a flash, it gets removed by trimming. Additional finishing processes such as machining, polishing, or coating are necessary to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
7) Quality Inspection
Then, the parts are examined for quality, dimensional accuracy, and defects, including non-destructive testing, visual inspections, and measurements.
Any excess or scrap material generated during the process can be recycled and reused. The process can be repeated continuously, with the same mold used to produce many identical parts.
The tools present in the process are crucial for working the Die-Casting Machine. They are:
Tools
Die or Mold
This tool consists of mainly two components: the fixed half (cover die) and the moving half (ejector die), which are precisely machined to create the desired shape. The mold is formed from materials capable of withstanding high pressures and temperatures.
- The Cover Die
The fixed half, also known as the Cover Die or the stationery Die, is placed securely in the Die Casting Machine and remains stationary throughout the process. It has cavities, cores, and other features which mold the molten metal.
- The Ejector Die
The Ejector Die, or the moving half, is a part of the die that can move in and out of the clamping unit. It includes the ejector pins or the ejector plates, which help the solidified part to push out of the mold.
Furnace
The furnace is used for melting the metal alloys used in the die casting process and is designed to ensure that the metal does not overheat and is at the required temperature. The furnace has a part inside that holds the metal, called the crucible.
Injection System
The Injection System helps to force the molten metal out of the mold cavity. The Injection System consists of three components, i.e., The Hydraulic Piston or The Plunger, the Shot Chamber, and the Injection cylinder.
The Hydraulic Piston is responsible for pushing the metal out of the cold chamber into the mold cavity by its hydraulic pressure. The Shot Chamber is where the metal is placed before it is injected into the mold. The Injection Cylinder contains the hydraulic piston and helps it provide pressure for the molten metal to move in the mold.
Trimming Tools
Trimming tools are used to remove any excess material that forms along the line of the cast. The excess part is known as a flash, and it is created by the gap between the two halves, which results in metal escaping and solidifying. The trimming tools help in several ways, like flash removal, dimensional accuracy, surface finishing, and polishing.
Ejector System
The Ejector System helps ensure the safe ejecting of the metal parts from the mold so they can be processed further. The Ejector System consists of mainly two components, i.e., The Ejector Pins and The Ejector Plates. These pins or plates come in contact with the solidified metal to push it out of the mold. They actuate by an Ejector mechanism, which helps move the pins and plates systemically.
Cold Chamber
The Cold Chamber is one of the most central parts of the Cold Chamber Machine. It transfers the molten metal into the mold cavity under high pressure in the casting process.
Platen
The platen is a large, flat, rectangular plate supporting mold stability. The platen is responsible for securing and holding the fixed half of the mold (the cover die) in place during the casting process. It plays a crucial role in ensuring that the mold remains closed under the high pressure of the molten metal injection. The platen ensures precise alignment and parallelism between the two halves of the mold (cover die and ejector die). Proper alignment is essential for maintaining quality and dimensional accuracy.
Lubrication
Lubrication in cold chamber die casting is to aid in the release of the finished part from the mold cavity. Lubricants help reduce friction between the mold surfaces and the solidified metal, resulting in more effortless and better consistent part Ejection.
There are four types of lubricants: Graphite Lubricants, Water Based Lubricants, Spray Lubricants, and Solid Lubricants. Lubricants also help reduce wear and tear on the mold components, such as the cover die, and ejector die. Continuous contact between the molten metal and the mold can lead to surface erosion and damage. Lubrication helps extend the life of the mold by minimizing wear and tear.
Shot Control System
This system measures and controls the volume of molten metal injected into the mold, ensuring consistency. Shot control ensures consistent part dimensions and quality across multiple casting cycles.
Clamping Unit
The clamping unit holds the die halves together during the casting process.
Advantages of the Cold Chamber Die Casting
There are numerous advantages of Cold Chamber Die-casting, such as:
Used for High Melting Points and Diverse Metals
The Cold Chamber Die-Casting method uses metals with high melting points, such as aluminum, copper, brass, and zinc. It helps for the production of diverse metals with different properties.
Excellent Dimensional Accuracy
The general tolerance class of Die-Casting parts is IT13~IT15 in GB/T 1800-2009, and the higher precision can reach IT10~W 1 1. Due to the high dimensional accuracy of the Cold Chamber, Die Casting can achieve tight tolerances and excellent dimensional accuracy, making it suitable for parts that require precision.
High Surface Finish
Cold Chamber Die Casting can produce parts with a smooth and polished surface finish, reducing the need for additional finishing and polishing. Cold Chamber Die casting relies on precise dies with highly polished cavity surfaces. These dies are designed to replicate the desired shape and finish of the part. The smoothness of the die surfaces directly transfers to the cast part’s surface, resulting in a smooth finish.
Production Efficiency
This process is soundest for high-volume production due to its quick cycle times. It can produce a large number of parts in a short amount of time. This results in cost and time savings in large-scale manufacturing companies.
Good Material Properties
Die-cast parts display desirable material properties, such as high strength, remarkable corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity—Cold Chamber Die Casting results in excellent dimensional accuracy. The precise design of the die and the specific molten designs help create high-accuracy and well-polished metal products. The quality of metals produced through cold chamber die casting often exhibits excellent mechanical properties, including high strength, hardness, and durability.
Cost-Effective for Large Companies
The initial tooling costs can be high, but Cold Chamber Die Casting becomes cost-effective when producing large quantities due to its high-speed production abilities. Cold Chamber Die Casting is a highly efficient process capable of producing many parts in a comparatively short time. This high production rate translates to economies of scale, reducing the cost per part when producing large quantities. Cold Chamber Die Casting generates minimal material waste. The excess material from each casting can often be recycled, reducing material costs and waste disposal expenses.
Applications of Cold Chamber Die Casting
Cold Chamber Die Casting is applicable in various industries due to its versatility, precision, and efficiency in producing complex, high-quality metal components. Some of the sectors are:
Automotive Industry
Automotive parts make up a vehicle, serving various functions to ensure automobiles’ proper operation, safety, and functionality. Cold Chamber Die Casting helps manufacture engine components, braking systems, exhaust systems, electronics, and many more products.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry frequently relies on Cold Chamber Die Casting as a manufacturing process to produce critical components and parts for aircraft and spacecraft. Cold Chamber Die Casting offers several advantages that align with the high precision, quality, and performance standards required in aerospace applications.
Electronics Industry
The electronics sector relies on Cold Chamber Die Casting for manufacturing components like heat sinks, connectors, and enclosures. This process ensures efficient heat dissipation and electrical conductivity, which is crucial for electronic devices.
Medical Device Industry
Medical devices demand precision and biocompatibility. Cold Chamber Die Casting is used for producing surgical instruments, imaging equipment components, and other medical devices requiring high-quality, intricate metal parts.
Consumer Electronics
Manufacturers benefit from Cold Chamber Die Casting for creating casings and components of smartphones, laptops, and other consumer electronic devices.
Also check: A Comprehensive Guide to Cold Chamber Die Casting Process
Conclusion
A Cold Chamber Die-Casting Machine is essential for manufacturing high-quality, diverse metal parts. It offers several advantages for the production and the company. It is best for large-scale companies that want to work with a wide range of metal alloys, excellent surface finish, and efficient production rates.
Cold chamber die casting applies to various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods, requiring intricately designed metal parts. To get the best quality results, Marcus Hi-Tech Engineering is a global leader who can help you climb the ladder in your industry. Their commitment to providing precision quality components is unmatched.
FAQs
Cold Chamber Die Casting is a metal casting process used to produce complex, high-quality, and dimensionally accurate parts made from non-ferrous metals like aluminum, magnesium, and copper alloys. It involves injecting molten metal into a die cavity under high pressure to create a precisely shaped product.
In Cold Chamber Die Casting, the metal is melted in a separate furnace and then transferred to the injection chamber. In contrast, Hot Chamber Die Casting melts the metal within the casting machine itself. Cold Chamber Die Casting is typically used for metals with higher melting points.
Some advantages include:
- Suitable for a wide range of metals, especially those with high melting points.
- Produces high-strength, durable parts with excellent surface finishes.
- Allows for intricate and detailed part designs.
- Minimal porosity in the finished products.
- Minimal heat-related damage to the die.
Limitations include:
- Slower cycle times compared to Hot Chamber Die Casting.
- Higher initial setup costs due to the need for a separate melting furnace.
- Limited to non-ferrous metals.
- Tooling and die maintenance can be costly.


